
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Drug/Regimen
- A Real-World Study of Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Lobeglitazone in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Bo-Yeon Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Suk Kyeong Kim, Jung-Hyun Noh, Cheol-Young Park, Hyeong-Kyu Park, Kee-Ho Song, Jong Chul Won, Jae Myung Yu, Mi Young Lee, Jae Hyuk Lee, Soo Lim, Sung Wan Chun, In-Kyung Jeong, Choon Hee Chung, Seung Jin Han, Hee-Seok Kim, Ju-Young Min, Sungrae Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):855-865. Published online March 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0264
- 6,706 View
- 296 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) have been associated with various safety concerns including weight gain, bladder cancer, and congestive heart failure (CHF). This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of lobeglitazone, a novel TZD in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in real practice.
Methods
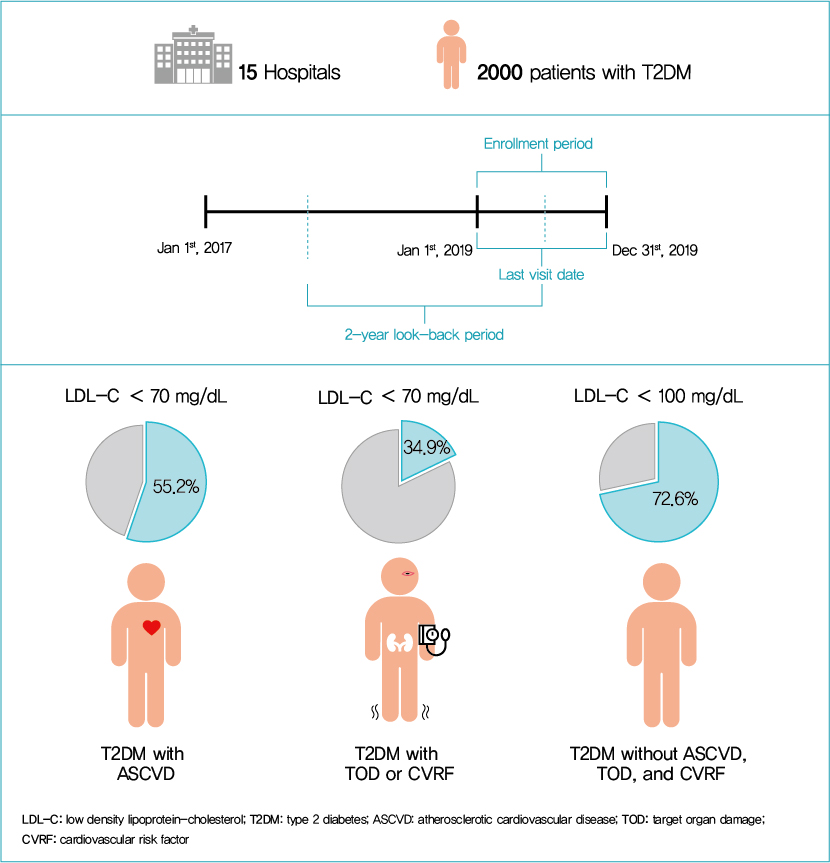
In this non-interventional, multi-center, retrospective, and observational study conducted at 15 tertiary or secondary referral hospitals in Korea, a total of 2,228 patients with T2DM who received lobeglitazone 0.5 mg for more than 1 year were enrolled.
Results
Overall adverse events (AEs) occurred in 381 patients (17.10%) including edema in 1.97% (n=44). Cerebrovascular and cardiovascular diseases were identified in 0.81% (n=18) and 0.81% (n=18), respectively. One case of CHF was reported as an AE. Edema occurred in 1.97% (n=44) of patients. Hypoglycemia occurred in 2.47% (n=55) of patients. Fracture occurred in 1.17% (n=26) of all patients. Lobeglitazone significantly decreased HbA1c level, resulting in a mean treatment difference of -1.05%± 1.35% (P<0.001), and decreased total cholesterol, triglyceride, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. However, it increased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, regardless of statin administration. The patients who received lobeglitazone 0.5 mg showed an apparent reduction in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) from baseline during the first 6 months of treatment. The HbA1c levels remained stable between months 6 and 42.
Conclusion
Lobeglitazone has long-term safety profile, good glycemic-lowering effect and long-term durability of glycemic control in real-world clinical settings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and safety of novel thiazolidinedione lobeglitazone for managing type-2 diabetes a meta-analysis
Deep Dutta, Saptarshi Bhattacharya, Manoj Kumar, Priyankar K. Datta, Ritin Mohindra, Meha Sharma
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(1): 102697. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of lobeglitazone, a new Thiazolidinedione, as compared to the standard of care in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Shashank R. Joshi, Saibal Das, Suja Xaviar, Shambo Samrat Samajdar, Indranil Saha, Sougata Sarkar, Shatavisa Mukherjee, Santanu Kumar Tripathi, Jyotirmoy Pal, Nandini Chatterjee
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(1): 102703. CrossRef - Will lobeglitazone rival pioglitazone? A systematic review and critical appraisal
Kalyan Kumar Gangopadhyay, Awadhesh Kumar Singh
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(4): 102747. CrossRef - Lobeglitazone
Reactions Weekly.2023; 1948(1): 262. CrossRef - Lobeglitazone, a novel thiazolidinedione, for secondary prevention in patients with ischemic stroke: a nationwide nested case-control study
Joonsang Yoo, Jimin Jeon, Minyoul Baik, Jinkwon Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Lobeglitazone and Its Therapeutic Benefits: A Review
Balamurugan M, Sarumathy S, Robinson R
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Oldies but Goodies: Thiazolidinedione as an Insulin Sensitizer with Cardioprotection
Eun-Hee Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 827. CrossRef
- Efficacy and safety of novel thiazolidinedione lobeglitazone for managing type-2 diabetes a meta-analysis
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Current Status of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Target Achievement in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea Compared with Recent Guidelines
- Soo Jin Yun, In-Kyung Jeong, Jin-Hye Cha, Juneyoung Lee, Ho Chan Cho, Sung Hee Choi, SungWan Chun, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sang Soo Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Gwanpyo Koh, Su Kyoung Kwon, Jae Hyuk Lee, Min Kyong Moon, Junghyun Noh, Cheol-Young Park, Sungrae Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):464-475. Published online March 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0088
- 6,950 View
- 347 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We evaluated the achievement of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) targets in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) according to up-to-date Korean Diabetes Association (KDA), European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS), and American Diabetes Association (ADA) guidelines.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study collected electronic medical record data from patients with T2DM (≥20 years) managed by endocrinologists from 15 hospitals in Korea (January to December 2019). Patients were categorized according to guidelines to assess LDL-C target achievement. KDA (2019): Very High-I (atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [ASCVD]) <70 mg/dL; Very High-II (target organ damage [TOD], or cardiovascular risk factors [CVRFs]) <70 mg/dL; high (others) <100 mg/dL. ESC/EAS (2019): Very High-I (ASCVD): <55 mg/dL; Very High-II (TOD or ≥3-CVRF) <55 mg/dL; high (diabetes ≥10 years without TOD plus any CVRF) <70 mg/dL; moderate (diabetes <10 years without CVRF) <100 mg/dL. ADA (2019): Very High-I (ASCVD); Very High-II (age ≥40+ TOD, or any CVRF), for high intensity statin or statin combined with ezetimibe.
Results
Among 2,000 T2DM patients (mean age 62.6 years; male 55.9%; mean glycosylated hemoglobin 7.2%) ASCVD prevalence was 24.7%. Of 1,455 (72.8%) patients treated with statins, 73.9% received monotherapy. According to KDA guidelines, LDL-C target achievement rates were 55.2% in Very High-I and 34.9% in Very High-II patients. With ESC/EAS guidelines, target attainment rates were 26.6% in Very High-I, 15.7% in Very High-II, and 25.9% in high risk patients. Based on ADA guidelines, most patients (78.9%) were very-high risk; however, only 15.5% received high-intensity statin or combination therapy.
Conclusion
According to current dyslipidemia management guidelines, LDL-C goal achievement remains suboptimal in Korean patients with T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk factor control and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Do Kyeong Song, Young Sun Hong, Yeon-Ah Sung, Hyejin Lee, Hidetaka Hamasaki
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(2): e0299035. CrossRef - Distinct effects of rosuvastatin and rosuvastatin/ezetimibe on senescence markers of CD8+ T cells in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial
Sang-Hyeon Ju, Joung Youl Lim, Minchul Song, Ji Min Kim, Yea Eun Kang, Hyon-Seung Yi, Kyong Hye Joung, Ju Hee Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Bon Jeong Ku
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(1): 12. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - Association between carotid atherosclerosis and presence of intracranial atherosclerosis using three-dimensional high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, You-Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeong Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, Geon-Ho Jahng, Soonchan Park, In-Kyung Jeong, Chang-Woo Ryu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 191: 110067. CrossRef
- Risk factor control and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Drug/Regimen
- Comprehensive Review of Current and Upcoming Anti-Obesity Drugs
- Jang Won Son, Sungrae Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):802-818. Published online December 23, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0258

- 15,283 View
- 976 Download
- 54 Web of Science
- 62 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Obesity is among the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide and its prevalence continues to increase globally. Because obesity is a chronic, complex, and heterogeneous disease influenced by genetic, developmental, biological, and environmental factors, it is necessary to approach obesity with an integrated and comprehensive treatment strategy. As it is difficult to achieve and sustain successful long-term weight loss in most patients with obesity through lifestyle modifications (e.g., diet, exercise, and behavioral therapy), pharmacological approaches to the treatment of obesity should be considered as an adjunct therapy. Currently, four drugs (orlistat, naltrexone extended-release [ER]/bupropion ER, phentermine/topiramate controlled-release, and liraglutide) can be used long-term (>12 weeks) to promote weight loss by suppressing appetite or decreasing fat absorption. Pharmacotherapy for obesity should be conducted according to a proper assessment of the clinical evidence and customized to individual patients considering the characteristics of each drug and comorbidities associated with obesity. In this review, we discuss the mechanisms of action, efficacy, and safety of these available long-term anti-obesity drugs and introduce other potential agents under investigation. Furthermore, we discuss the need for research on personalized obesity medicine.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Shedding light on weight loss: A narrative review of medications for treating obesity
Haritha Darapaneni, Samridhi Lakhanpal, Hiren Chhayani, Kinna Parikh, Meet Patel, Vasu Gupta, Fnu Anamika, Ripudaman Munjal, Rohit Jain
Romanian Journal of Internal Medicine.2024; 62(1): 3. CrossRef - Projected health and economic effects of the increase in childhood obesity during the COVID-19 pandemic in England: The potential cost of inaction
Iván Ochoa-Moreno, Ravita Taheem, Kathryn Woods-Townsend, Debbie Chase, Keith M. Godfrey, Neena Modi, Mark Hanson, Rebecca F. Baggaley
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(1): e0296013. CrossRef - Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: a selective review of pathogenesis, diagnostic approaches, and therapeutic strategies
Mohammad Habibullah, Khaleed Jemmieh, Amr Ouda, Mohammad Zulqurnain Haider, Mohammed Imad Malki, Abdel-Naser Elzouki
Frontiers in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A review of an investigational drug retatrutide, a novel triple agonist agent for the treatment of obesity
Manmeet Kaur, Saurav Misra
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.2024; 80(5): 669. CrossRef - Gut microbiota and therapy for obesity and type 2 diabetes
Luyao Zhang, Pai Wang, Juan Huang, Yanpeng Xing, F. Susan Wong, Jian Suo, Li Wen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Adipocyte-targeted delivery of rosiglitazone with localized photothermal therapy for the treatment of diet-induced obesity in mice
Yunxiao Zhang, Maoqi Luo, Yaxin Jia, Tingting Gao, Li Deng, Tao Gong, Zhirong Zhang, Xi Cao, Yao Fu
Acta Biomaterialia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Surgery is associated with better long-term outcomes than pharmacological treatment for obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Leonardo Zumerkorn Pipek, Walter Augusto Fabio Moraes, Rodrigo Massato Nobetani, Vitor Santos Cortez, Alberto Santos Condi, João Victor Taba, Rafaela Farias Vidigal Nascimento, Milena Oliveira Suzuki, Fernanda Sayuri do Nascimento, Vitoria Carneiro de Mat
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of endoscopic resuturing versus pharmacotherapy to treat weight recidivism after endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty
Kaveh Hajifathalian, Okeefe Simmons, Mohamed Abu-Hammour, Kamal Hassan, Reem Z. Sharaiha
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2023; 98(6): 944. CrossRef - Gardenia fruit and Eucommia leaves combination improves hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia via pancreatic lipase and AMPK-PPARα and Keap-1-Nrf2-HO-1 regulation
Xiaotong Su, Shun Hao, Wenna Li, Xu Li, Zhentao Mo, Yiqi Li, Lu Xiao, Wenjun Wang, Feng Wang
Journal of Functional Foods.2023; 100: 105394. CrossRef - Targeting fatty acid synthase modulates sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib via ferroptosis
Yan Li, Wenjuan Yang, Yuanyuan Zheng, Weiqi Dai, Jie Ji, Liwei Wu, Ziqi Cheng, Jie Zhang, Jingjing Li, Xuanfu Xu, Jianye Wu, Mingwei Yang, Jiao Feng, Chuanyong Guo
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diet-induced gut dysbiosis and inflammation: Key drivers of obesity-driven NASH
Gideon G. Kang, Natalie L. Trevaskis, Andrew J. Murphy, Mark A. Febbraio
iScience.2023; 26(1): 105905. CrossRef - The gut microbiota in obesity and weight management: microbes as friends or foe?
Matthias Van Hul, Patrice D. Cani
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2023; 19(5): 258. CrossRef - Phase I studies of the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the dual glucagon receptor/glucagon‐like peptide‐1 receptor agonistBI456906
Arvid Jungnik, Jorge Arrubla Martinez, Leona Plum‐Mörschel, Christoph Kapitza, Daniela Lamers, Claus Thamer, Corinna Schölch, Michael Desch, Anita M. Hennige
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(4): 1011. CrossRef - From Metabolic Syndrome to Type 2 Diabetes in Youth
Dario Iafusco, Roberto Franceschi, Alice Maguolo, Salvatore Guercio Nuzio, Antonino Crinò, Maurizio Delvecchio, Lorenzo Iughetti, Claudio Maffeis, Valeria Calcaterra, Melania Manco
Children.2023; 10(3): 516. CrossRef - Excess body weight: Novel insights into its roles in obesity comorbidities
Xiang Zhang, Suki Ha, Harry Cheuk-Hay Lau, Jun Yu
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2023; 92: 16. CrossRef - Striatal dopamine D2-like receptors availability in obesity and its modulation by bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Gabriela Ribeiro, Ana Maia, Gonçalo Cotovio, Francisco P. M. Oliveira, Durval C. Costa, Albino J. Oliveira-Maia
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cost-effectiveness analysis of five anti-obesity medications from a US payer's perspective
Ainhoa Gómez Lumbreras, Malinda S. Tan, Lorenzo Villa-Zapata, Sabrina Ilham, Jacob C. Earl, Daniel C. Malone
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2023; 33(6): 1268. CrossRef - Analysis of Serious Weight Gain in Patients Using Alectinib for ALK-Positive Lung Cancer
Simon P. de Leeuw, Melinda A. Pruis, Barend J. Sikkema, Mostafa Mohseni, G. D. Marijn Veerman, Marthe S. Paats, Daphne W. Dumoulin, Egbert F. Smit, Annemie M.W. J. Schols, Ron H.J. Mathijssen, Elisabeth F.C. van Rossum, Anne-Marie C. Dingemans
Journal of Thoracic Oncology.2023; 18(8): 1017. CrossRef - Role of flavonoids in controlling obesity: molecular targets and mechanisms
Anns Mahboob, Samson Mathews Samuel, Arif Mohamed, Mohmmad Younus Wani, Sofiane Ghorbel, Nabil Miled, Dietrich Büsselberg, Ali Chaari
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The N-degron pathway mediates lipophagy: The chemical modulation of lipophagy in obesity and NAFLD
Eui Jung Jung, Ki Woon Sung, Tae Hyun Bae, Hee-Yeon Kim, Ha Rim Choi, Sung Hyun Kim, Chan Hoon Jung, Su Ran Mun, Yeon Sung Son, Shin Kim, Young Ho Suh, Anna Kashina, Joo-Won Park, Yong Tae Kwon
Metabolism.2023; 146: 155644. CrossRef - Bupropion Mediated Effects on Depression, Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, and Smoking Cessation
Austin Clark, Brendan Tate, Bretton Urban, Ryan Schroeder, Sonja Gennuso, Shahab Ahmadzadeh, David McGregor, Brook Girma, Sahar Shekoohi, Alan D. Kaye
Health Psychology Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent advancements in pharmacological strategies to modulate energy balance for combating obesity
Benudhara Pati, Satyabrata Sendh, Bijayashree Sahu, Sunil Pani, Nivedita Jena, Naresh Chandra Bal
RSC Medicinal Chemistry.2023; 14(8): 1429. CrossRef - Management of abdominal wall hernias in patients with severe obesity
Omar M. Ghanem, Sean Orenstein, S. Julie-Ann Lloyd, Amin Andalib, Alice Race, Holly Ann Burt, Farah Husain, Matthew Goldblatt, Matthew Kroh
Surgical Endoscopy.2023; 37(9): 6619. CrossRef - Obesity-related hypertension and chronic kidney disease: from evaluation to management
Mi-Hyang Jung, Sang-Hyun Ihm
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 42(4): 431. CrossRef - Antiepileptics pharmacotherapy or antidiabetics may hold potential in treatment of epileptic patients with diabetes mellitus: A narrative review
Marwan AL-NİMER, Saeed AL-ZUHAİRY
Hacettepe University Journal of the Faculty of Pharmacy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Medicamentos antidiabéticos utilizados com a finalidade de perda de peso
Sâmia Moreira de ANDRADE, Maria Victória Macedo de ANDRADE, Pedro Henrique Almeida de FARIA, Luís Marcelo Vieira ROSA, Plínio Robson Cavalcante COSTA, Luiz Gustavo Freitas PIRES
Diversitas Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Treatment of hypothalamic obesity in people with hypothalamic injury: new drugs are on the horizon
Christian L. Roth, Anna Zenno
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity: What’s Old, What’s New and How We Manage It: An Integrated Approach in Pharmacy Practice
Ângelo Jesus
FarmaJournal.2023; 8(2): 45. CrossRef - Integrating Pharmacotherapy and Psychotherapy for Weight Loss
Marla Sanzone, Morgan Sammons
Journal of Health Service Psychology.2023; 49(4): 177. CrossRef - Effect of Lingguizhugan decoction in activating fat mobilization in obesity
Yubin YANG, Yunlong WANG, Zhengbang SUN, Ting DU, Ying YANG, Jiaojiao CHEN, Meiling WANG, Hairong LI, Jian QIN
Journal of Holistic Integrative Pharmacy.2022; 3(1): 68. CrossRef - Computational approaches to predicting treatment response to obesity using neuroimaging
Leonard Kozarzewski, Lukas Maurer, Anja Mähler, Joachim Spranger, Martin Weygandt
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2022; 23(4): 773. CrossRef - Delivery of miRNAs to the adipose organ for metabolic health
Karin Kornmueller, Ez-Zoubir Amri, Marcel Scheideler, Ruth Prassl
Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews.2022; 181: 114110. CrossRef - Purple sweet potato leaf extracts suppress adipogenic differentiation of human bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stem cells
Masakazu Ishii, Nao Ikeda, Haruka Miyata, Manami Takahashi, Masahiro Nishimura
Journal of Food Biochemistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Anti-Adiposity Mechanisms of Ampelopsin and Vine Tea Extract in High Fat Diet and Alcohol-Induced Fatty Liver Mouse Models
Jianbo Wu, Kenchi Miyasaka, Wakana Yamada, Shogo Takeda, Norihito Shimizu, Hiroshi Shimoda
Molecules.2022; 27(3): 607. CrossRef - Pharmacotherapeutic options in pediatric obesity: an urgent call for further research
María Florencia González Bagnes, Claudio González, Valeria Hirschler, Guillermo Di Girolamo
Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy.2022; 23(8): 869. CrossRef - Russelioside B: a Pregnane Glycoside with Pharmacological Potential
Essam Abdel-Sattar, Dalia E. Ali
Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia.2022; 32(2): 188. CrossRef - Pharmacotherapy in Childhood Obesity
Peter Kühnen, Heike Biebermann, Susanna Wiegand
Hormone Research in Paediatrics.2022; 95(2): 177. CrossRef - Effects of Vinegar/Acetic Acid Intake on Appetite Measures and Energy Consumption: Systematic Review
Faten O. Hasan, Kristen P. Hamilton, Siddhartha S. Angadi, Sibylle Kranz
Translational Journal of the American College of Sports Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Renaming NAFLD to MAFLD: Advantages and Potential Changes in Diagnosis, Pathophysiology, Treatment, and Management
Fajuan Rui, Hongli Yang, Xinyu Hu, Qi Xue, Yayun Xu, Junping Shi, Jie Li
Infectious Microbes and Diseases.2022; 4(2): 49. CrossRef - Treatments for obesity in the context of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and mental health
Aadi Sharma, Somaya Albhaisi, Arun J. Sanyal
Clinical Liver Disease.2022; 20(2): 48. CrossRef - A narrative review of anti-obesity medications for obese patients with osteoarthritis
Win Min Oo, Ali Mobasheri, David J Hunter
Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy.2022; 23(12): 1381. CrossRef - Sulfated Glucan from the Green Seaweed Caulerpa sertularioides Inhibits Adipogenesis through Suppression of Adipogenic and Lipogenic Key Factors
Gildacio Chaves Filho, Lucas Batista, Silvia de Medeiros, Hugo Rocha, Susana Moreira
Marine Drugs.2022; 20(8): 470. CrossRef - Clinical Impact of Semaglutide, a Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist, on Obesity Management: A Review
Nasser M Alorfi, Alanood S Algarni
Clinical Pharmacology: Advances and Applications.2022; Volume 14: 61. CrossRef - The Role of Gut Microbiota Modulation Strategies in Obesity: The Applications and Mechanisms
Lingyue Shan, Akanksha Tyagi, Umair Shabbir, Xiuqin Chen, Selvakumar Vijayalakshmi, Pianpian Yan, Deog-Hwan Oh
Fermentation.2022; 8(8): 376. CrossRef - Orlistat and ezetimibe could differently alleviate the high-fat diet-induced obesity phenotype by modulating the gut microbiota
Jin Jin, Jiani Wang, Ruyue Cheng, Yan Ren, Zhonghua Miao, Yating Luo, Qingqing Zhou, Yigui Xue, Xi Shen, Fang He, Haoming Tian
Frontiers in Microbiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - N-linoleyltyrosine ameliorates high-fat diet-induced obesity in C57BL/6 mice via cannabinoid receptor regulation
Zheng-yu Yang, Yi-ying Wu, Yi Zhou, Yun-qi Yang, Jia-hui Zhang, Tao He, Sha Liu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Anti-obesity pharmacotherapy for treatment of pediatric type 2 diabetes: Review of the literature and lessons learned from adults
Megan O. Bensignor, Aaron S. Kelly, Silva Arslanian
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Blockade of CXXC5-dishevelled interaction inhibits adipogenic differentiation, obesity, and insulin resistance in mice
Seol Hwa Seo, Dasung Lee, Soung-Hoon Lee, Kang-Yell Choi
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of the Melanocortin 4-Receptor Ile269Asn Mutation on Weight Loss Response to Dietary, Phentermine and Bariatric Surgery Interventions
Itzel G. Salazar-Valencia, Hugo Villamil-Ramírez, Francisco Barajas-Olmos, Martha Guevara-Cruz, Luis R. Macias-Kauffer, Humberto García-Ortiz, Omar Hernández-Vergara, David Alberto Díaz de Sandy-Galán, Paola León-Mimila, Federico Centeno-Cruz, Luis E. Gon
Genes.2022; 13(12): 2267. CrossRef - A Nephrologist Perspective on Obesity: From Kidney Injury to Clinical Management
Clara García-Carro, Ander Vergara, Sheila Bermejo, María A. Azancot, Joana Sellarés, Maria José Soler
Frontiers in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Phentermine-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Secondary to Uncontrolled Hypertension in a Patient with Weight Regain Post-bariatric Surgery
Marvin Wei Jie Chua, Boon Cheok Lai
Obesity Surgery.2021; 31(8): 3874. CrossRef - BMI Course Over 10 Years After Bariatric Surgery and Biopsychosocial Complexity Assessed with the INTERMED: a Retrospective Study
Yann Corminboeuf, Beate Wild, Catherine Zdrojewski, Dieter Schellberg, Lucie Favre, Michel Suter, Friedrich Stiefel
Obesity Surgery.2021; 31(9): 3996. CrossRef - The Role of Positron Emission Tomography in Bariatric Surgery Research: a Review
Jason Bini, Mathieu Norcross, Maija Cheung, Andrew Duffy
Obesity Surgery.2021; 31(10): 4592. CrossRef - Anti-Obesity Effect of Hot Water Extract of Barley Sprout through the Inhibition of Adipocyte Differentiation and Growth
Myeong-Jin Kim, Hye-Won Kawk, Sang-Hyeon Kim, Hyo-Jae Lee, Ji-Won Seo, Jong-Tae Kim, Seung-Hee Jang, Min-Jeong Kim, Young-Min Kim
Metabolites.2021; 11(9): 610. CrossRef - Anti-Obesity Effect of Polygalin C Isolated from Polygala japonica Houtt. via Suppression of the Adipogenic and Lipogenic Factors in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
Wona Jee, Seung-Hyeon Lee, Hyun Min Ko, Ji Hoon Jung, Won-Seok Chung, Hyeung-Jin Jang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(19): 10405. CrossRef - The cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor Roscovitine prevents diet-induced metabolic disruption in obese mice
Nabil Rabhi, Kathleen Desevin, Briana Noel Cortez, Ryan Hekman, Jean Z. Lin, Andrew Emili, Stephen R. Farmer
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Chlorogenic Acids Inhibit Adipogenesis: Implications of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
Mengting Liu, Jian Qin, Jing Cong, Yubin Yang, Muhittin Yurekli
International Journal of Endocrinology.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Médicaments anti-obésité : leçons des échecs pour l’avenir
André J. Scheen
Médecine des Maladies Métaboliques.2021; 15(8): 734. CrossRef - Obesity and Eating Disorders in Children and Adolescents: The Bidirectional Link
Stella Stabouli, Serap Erdine, Lagle Suurorg, Augustina Jankauskienė, Empar Lurbe
Nutrients.2021; 13(12): 4321. CrossRef - MEK6 Overexpression Exacerbates Fat Accumulation and Inflammatory Cytokines in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity
Suyeon Lee, Myoungsook Lee
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(24): 13559. CrossRef - Skin and obesity in childhood: an update
Valeria Hirschler
AIMS Medical Science.2021; 8(4): 311. CrossRef - An Avocado Extract Enriched in Mannoheptulose Prevents the Negative Effects of a High-Fat Diet in Mice
Paul J. Pistell, Tadanobu Utsuki, Joseph Francis, Philip J. Ebenezer, Jennifer Terrebonne, George S. Roth, Donald K. Ingram
Nutrients.2021; 14(1): 155. CrossRef
- Shedding light on weight loss: A narrative review of medications for treating obesity
- Response: Clinical Characteristics of People with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes between 2015 and 2016: Difference by Age and Body Mass Index (
Diabetes Metab J 2018;42:137-46) - Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Sungrae Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(3):251-253. Published online June 19, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0099
- 3,848 View
- 43 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
- Epidemiology
- Clinical Characteristics of People with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes between 2015 and 2016: Difference by Age and Body Mass Index
- Kyoung Hwa Ha, Cheol Young Park, In Kyung Jeong, Hyun Jin Kim, Sang-Yong Kim, Won Jun Kim, Ji Sung Yoon, In Joo Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Sungrae Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(2):137-146. Published online February 14, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.42.2.137
- 5,358 View
- 80 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background We evaluated the clinical characteristics of insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction in newly diagnosed, drug-naive people with type 2 diabetes by analyzing nationwide cross-sectional data.
Methods We collected the clinical data of 912 participants with newly diagnosed diabetes from 83 primary care clinics and hospitals nationwide from 2015 to 2016. The presence of insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction was defined as a homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) value ≥2.5 and fasting C-peptide levels <1.70 ng/mL, respectively.
Results A total of 75.1% and 22.6% of participants had insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction, respectively. The proportion of participants with insulin resistance but no β-cell dysfunction increased, and the proportion of participants with β-cell dysfunction but no insulin resistance decreased as body mass index (BMI) increased. People diagnosed with diabetes before 40 years of age had significantly higher HOMA-IR and BMI than those diagnosed over 65 years of age (HOMA-IR, 5.0 vs. 3.0; BMI, 28.7 kg/m2 vs. 25.1 kg/m2). However, the β-cell function indices were lower in people diagnosed before 40 years of age than in those diagnosed after 65 years of age (homeostatic model assessment of β-cell function, 39.3 vs. 64.9; insulinogenic index, 10.3 vs. 18.7; disposition index, 0.15 vs. 0.25).
Conclusion We observed that the main pathogenic mechanism of type 2 diabetes is insulin resistance in participants with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. In addition, young adults with diabetes are more likely to have higher insulin resistance with obesity and have higher insulin secretory defect with severe hyperglycemia in the early period of diabetes than older populations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A double‐blind, Randomized controlled trial on glucose‐lowering EFfects and safety of adding 0.25 or 0.5 mg lobeglitazone in type 2 diabetes patients with INadequate control on metformin and dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitor therapy: REFIND study
Soree Ryang, Sang Soo Kim, Ji Cheol Bae, Ji Min Han, Su Kyoung Kwon, Young Il Kim, Il Seong Nam‐Goong, Eun Sook Kim, Mi‐kyung Kim, Chang Won Lee, Soyeon Yoo, Gwanpyo Koh, Min Jeong Kwon, Jeong Hyun Park, In Joo Kim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(9): 1800. CrossRef - Apparent Insulin Deficiency in an Adult African Population With New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Davis Kibirige, Isaac Sekitoleko, Priscilla Balungi, William Lumu, Moffat J. Nyirenda
Frontiers in Clinical Diabetes and Healthcare.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Rising Incidence of Diabetes in Young Adults in South Korea: A National Cohort Study
Hyun Ho Choi, Giwoong Choi, Hojun Yoon, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 803. CrossRef - A Real-World Study of Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Lobeglitazone in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Bo-Yeon Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Suk Kyeong Kim, Jung-Hyun Noh, Cheol-Young Park, Hyeong-Kyu Park, Kee-Ho Song, Jong Chul Won, Jae Myung Yu, Mi Young Lee, Jae Hyuk Lee, Soo Lim, Sung Wan Chun, In-Kyung Jeong, Choon Hee Chung, Seung Jin Han, Hee-Seok Kim, Ju-Y
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 855. CrossRef - The Potential Effect of Rhizoma coptidis on Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking
Liyun Duan, De Jin, Xuedong An, Yuehong Zhang, Shenghui Zhao, Rongrong Zhou, Yingying Duan, Yuqing Zhang, Xinmin Liu, Fengmei Lian, Wen yi Kang
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - PRKAA2variation and the clinical characteristics of patients newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Dita Maria Virginia, Mae Sri Hartati Wahyuningsih, Dwi Aris Agung Nugrahaningsih
Asian Biomedicine.2021; 15(4): 161. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Pioglitazone versus Glimepiride after Metformin and Alogliptin Combination Therapy: A Randomized, Open-Label, Multicenter, Parallel-Controlled Study
Jeong Mi Kim, Sang Soo Kim, Jong Ho Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, Tae Nyun Kim, Soon Hee Lee, Chang Won Lee, Ja Young Park, Eun Sook Kim, Kwang Jae Lee, Young Sik Choi, Duk Kyu Kim, In Joo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 67. CrossRef - Favorable Glycemic Control with Once-Daily Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart after Changing from Basal Insulin in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes
Han Na Jang, Ye Seul Yang, Seong Ok Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Bo Kyung Koo, Hye Seung Jung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(4): 382. CrossRef - Insulin Resistance versus β-Cell Failure: Is It Changing in Koreans?
Mi-kyung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(2): 128. CrossRef - Response: Clinical Characteristics of People with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes between 2015 and 2016: Difference by Age and Body Mass Index (Diabetes Metab J2018;42:137-46)
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Sungrae Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(3): 251. CrossRef - Letter: Clinical Characteristics of People with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes between 2015 and 2016: Difference by Age and Body Mass Index (Diabetes Metab J 2018;42:137-46)
Ah Reum Khang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(3): 249. CrossRef
- A double‐blind, Randomized controlled trial on glucose‐lowering EFfects and safety of adding 0.25 or 0.5 mg lobeglitazone in type 2 diabetes patients with INadequate control on metformin and dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitor therapy: REFIND study
- Epidemiology
- Changing Clinical Characteristics according to Insulin Resistance and Insulin Secretion in Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetic Patients in Korea
- Jang Won Son, Cheol-Young Park, Sungrae Kim, Han-Kyu Lee, Yil-Seob Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(5):387-394. Published online October 22, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.5.387
- 3,799 View
- 67 Download
- 23 Web of Science
- 22 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The role of increased insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes has been emphasized in Asian populations. Thus, we evaluated the proportion of insulin resistance and the insulin secretory capacity in patients with early phase type 2 diabetes in Korea.
Methods We performed a cross-sectional analysis of 1,314 drug-naive patients with newly diagnosed diabetes from primary care clinics nationwide. The homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) was used as an index to measure insulin resistance, which was defined as a HOMA-IR ≥2.5. Insulin secretory defects were classified based on fasting plasma C-peptide levels: severe (<1.1 ng/mL), moderate (1.1 to 1.7 ng/mL) and mild to non-insulin secretory defect (≥1.7 ng/mL).
Results The mean body mass index (BMI) was 25.2 kg/m2; 77% of patients had BMIs >23.0 kg/m2. Up to 50% of patients had central obesity based on their waist circumference (≥90 cm in men and 85 cm in women), and 70.6% had metabolic syndrome. Overall, 59.5% of subjects had insulin resistance, and 20.2% demonstrated a moderate to severe insulin secretory defect. Among those with insulin resistance, a high proportion of subjects (79.0%) had a mild or no insulin secretory defect. Only 2.6% of the men and 1.9% of the women had both insulin resistance and a moderate to severe insulin secretory defect.
Conclusion In this study, patients with early phase type 2 diabetes demonstrated increased insulin resistance, but preserved insulin secretion, with a high prevalence of obesity and metabolic syndrome.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differences in health behavior and nutrient intake status between diabetes-aware and unaware Korean adults based on the Korea national health and nutrition examination survey 2016–18 data: A cross-sectional study
Anshul Sharma, Chen Lulu, Kee-Ho Song, Hae-Jeung Lee
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Plasma sphingomyelins increase in pre-diabetic Korean men with abdominal obesity
Seung-Soon Im, Hyeon Young Park, Jong Cheol Shon, In-Sung Chung, Ho Chan Cho, Kwang-Hyeon Liu, Dae-Kyu Song, Kyoung Heon Kim
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(3): e0213285. CrossRef - Lower Leg Fat Depots Are Associated with Albuminuria Independently of Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Metabolic Syndrome (Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 2008 to 2011)
Eugene Han, Nan Hee Cho, Mi Kyung Kim, Hye Soon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 461. CrossRef - Pathophysiology‐based phenotyping in type 2 diabetes: A clinical classification tool
Jacob V. Stidsen, Jan E. Henriksen, Michael H. Olsen, Reimar W. Thomsen, Jens S. Nielsen, Jørgen Rungby, Sinna P. Ulrichsen, Klara Berencsi, Johnny A. Kahlert, Søren G. Friborg, Ivan Brandslund, Aneta A. Nielsen, Jens S. Christiansen, Henrik T. Sørensen,
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of People with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes between 2015 and 2016: Difference by Age and Body Mass Index
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Cheol Young Park, In Kyung Jeong, Hyun Jin Kim, Sang-Yong Kim, Won Jun Kim, Ji Sung Yoon, In Joo Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Sungrae Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(2): 137. CrossRef - Gender specific association of parathyroid hormone and vitamin D with metabolic syndrome in population with preserved renal function
Min-Hee Kim, Jeongmin Lee, Jeonghoon Ha, Kwanhoon Jo, Dong-Jun Lim, Jung-Min Lee, Sang-Ah Chang, Moo-Il Kang, Bong Yun Cha
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Longitudinal Changes in Insulin Resistance, Beta-Cell Function and Glucose Regulation Status in Prediabetes
Chul-Hee Kim, Hong-Kyu Kim, Eun-Hee Kim, Sung-Jin Bae, Jaewon Choe, Joong-Yeol Park
The American Journal of the Medical Sciences.2018; 355(1): 54. CrossRef - Does Weight Gain Associated with Thiazolidinedione Use Negatively Affect Cardiometabolic Health?
Ki Dong Ko, Kyoung Kon Kim, Kyu Rae Lee
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2017; 26(2): 102. CrossRef - Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
Hyun Jin Kim, Seok O Park, Seung-Hyun Ko, Sang Youl Rhee, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Byung-Wan Lee, Jin Hwa Kim, Kyung Mook Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(6): 423. CrossRef - Prevalence of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions Is Associated With Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity
Suguru Mizuno, Hiroyuki Isayama, Yousuke Nakai, Takeharu Yoshikawa, Kazunaga Ishigaki, Saburo Matsubara, Natsuyo Yamamoto, Hideaki Ijichi, Keisuke Tateishi, Minoru Tada, Naoto Hayashi, Kazuhiko Koike
Pancreas.2017; 46(6): 801. CrossRef - Anatomic fat depots and cardiovascular risk: a focus on the leg fat using nationwide surveys (KNHANES 2008–2011)
Eugene Han, Yong-ho Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, In-Kyu Lee, Bong-Soo Cha
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Exenatide versus Insulin Lispro Added to Basal Insulin in a Subgroup of Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Kun-Ho Yoon, Elise Hardy, Jenny Han
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(1): 69. CrossRef - Protective effects of exercise training on endothelial dysfunction induced by total sleep deprivation in healthy subjects
Fabien Sauvet, Pierrick J Arnal, Pierre Emmanuel Tardo-Dino, Catherine Drogou, Pascal Van Beers, Clément Bougard, Arnaud Rabat, Garance Dispersyn, Alexandra Malgoyre, Damien Leger, Danielle Gomez-Merino, Mounir Chennaoui
International Journal of Cardiology.2017; 232: 76. CrossRef - Efficacy of Body Weight Reduction on the SGLT2 Inhibitor in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Hyun A Cho, Young Lee Jung, Yong Hoon Lee, Yu Chang Lee, Jung Eun Lee, Sol Jae Lee, Su Jin Jeong, Chong Hwa Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2017; 26(2): 107. CrossRef - Insulin Secretory Capacity and Insulin Resistance in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Jong-Dai Kim, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(3): 354. CrossRef - Long-Term Single and Joint Effects of Excessive Daytime Napping on the HOMA-IR Index and Glycosylated Hemoglobin
Xue Li, Xiuyu Pang, Qiao Zhang, Qiannuo Qu, Zhigang Hou, Zhipeng Liu, Lin Lv, Guanqiong Na, Wei Zhang, Changhao Sun, Ying Li
Medicine.2016; 95(5): e2734. CrossRef - Current status of managing diabetes mellitus in Korea
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2016; 31(5): 845. CrossRef - A Pilot Study Evaluating Steroid-Induced Diabetes after Antiemetic Dexamethasone Therapy in Chemotherapy-Treated Cancer Patients
Yusook Jeong, Hye Sook Han, Hyo Duk Lee, Jiyoul Yang, Jiwon Jeong, Moon Ki Choi, Jihyun Kwon, Hyun-Jung Jeon, Tae-Keun Oh, Ki Hyeong Lee, Seung Taik Kim
Cancer Research and Treatment.2016; 48(4): 1429. CrossRef - Clinical whole exome sequencing in early onset diabetes patients
Soo Heon Kwak, Chan-hyeon Jung, Chang Ho Ahn, Jungsun Park, Jeesoo Chae, Hye Seung Jung, Young Min Cho, Dae Ho Lee, Jong-Il Kim, Kyong Soo Park
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2016; 122: 71. CrossRef - Sleep extension increases IGF-I concentrations before and during sleep deprivation in healthy young men
Mounir Chennaoui, Pierrick J. Arnal, Catherine Drogou, Fabien Sauvet, Danielle Gomez-Merino
Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism.2016; 41(9): 963. CrossRef - 4-Hydroxyisoleucine: A Potential New Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Mohammad Ishraq Zafar, Feng Gao
BioDrugs.2016; 30(4): 255. CrossRef - Impairment of lysophospholipid metabolism in obesity: altered plasma profile and desensitization to the modulatory properties of n–3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in a randomized controlled trial
Josep M del Bas, Antoni Caimari, Maria Isabel Rodriguez-Naranjo, Caroline E Childs, Carolina Paras Chavez, Annette L West, Elizabeth A Miles, Lluis Arola, Philip C Calder
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.2016; 104(2): 266. CrossRef
- Differences in health behavior and nutrient intake status between diabetes-aware and unaware Korean adults based on the Korea national health and nutrition examination survey 2016–18 data: A cross-sectional study
- Clinical Care/Education
- Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Tale of Three Studies
- Jang Won Son, Sungrae Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(5):373-383. Published online October 22, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.5.373
- 4,594 View
- 55 Download
- 31 Web of Science
- 28 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) inhibitors have been touted as promising antihyperglycemic agents due to their beneficial effects on glycemia without inducing hypoglycemia or body weight gain and their good tolerability. Beyond their glucose-lowering effects, numerous clinical trials and experimental studies have suggested that DPP4 inhibitors may exert cardioprotective effects through their pleiotropic actions via glucagon-like peptide 1-dependent mechanisms or involving other substrates. Since 2008, regulatory agencies have required an assessment of cardiovascular disease (CVD) safety for the approval of all new anti-hyperglycemic agents, including incretin-based therapies. Three large prospective DPP4 inhibitor trials with cardiovascular (CV) outcomes have recently been published. According to the Saxagliptin Assessment of Vascular Outcomes Recorded in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus (SAVOR-TIMI 53) and EXamination of cArdiovascular outcoMes with alogliptIN versus standard of carE in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and acute coronary syndrome (EXAMINE) trials, DPP4 inhibitors, including saxagliptin and alogliptin, did not appear to increase the risk of CV events in patients with type 2 diabetes and established CVD or high risk factors. Unexpectedly, saxagliptin significantly increased the risk of hospitalization for heart failure by 27%, a finding that has not been explained and that requires further exploration. More recently, the Trial Evaluating Cardiovascular Outcomes with Sitagliptin (TECOS) trial demonstrated the CV safety of sitagliptin, including assessments of the primary composite CV endpoint and hospitalization for heart failure in patients with type 2 diabetes and established CVD. The CV outcomes of an ongoing linagliptin trial are expected to provide new evidence about the CV effects of a DPP4-inhibitor in patients with type 2 diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor Use is Associated with a Reduced Risk of Heart Failure Hospitalization in Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Real-World Study on a Diverse Urban Population
Weijia Li, Adarsh Katamreddy, Rachna Kataria, Merle L. Myerson, Cynthia C. Taub
Drugs - Real World Outcomes.2022; 9(1): 53. CrossRef - Comparative Cardiovascular Outcomes of SGLT2 Inhibitors in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Yu Jiang, Pingping Yang, Linghua Fu, Lizhe Sun, Wen Shen, Qinghua Wu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Baseline HbA1c With Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes: Analyses From DECLARE-TIMI 58
Avivit Cahn, Stephen D. Wiviott, Ofri Mosenzon, Erica L. Goodrich, Sabina A. Murphy, Ilan Yanuv, Aliza Rozenberg, Deepak L. Bhatt, Lawrence A. Leiter, Darren K. McGuire, John P.H. Wilding, Ingrid A.M. Gause-Nilsson, Anna Maria Langkilde, Marc S. Sabatine,
Diabetes Care.2022; 45(4): 938. CrossRef Effect of Switching from Linagliptin to Teneligliptin Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors in Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Eugene Han, Minyoung Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Hye Soon Kim, Byung-wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 4113. CrossRef- Effects of Teneligliptin on the Progressive Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Open-Label, Marker-Stratified Randomized, Parallel-Group Comparison, Standard Treatment-Controlled Multicenter Trial (TOPLEVEL
Miki Imazu, Atsushi Nakano, Shin Ito, Toshimitsu Hamasaki, Masafumi Kitakaze
Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy.2019; 33(3): 363. CrossRef - Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor use and risk of diabetic retinopathy: A population-based study
N.H. Kim, J. Choi, N.H. Kim, K.M. Choi, S.H. Baik, J. Lee, S.G. Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism.2018; 44(4): 361. CrossRef - Glucagon secretion determined by the RIA method is lower in patients with low left ventricular ejection fraction: The new glass study
Makoto Murata, Hitoshi Adachi, Taishuke Nakade, Shigeru Oshima
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2018; 144: 260. CrossRef - Coadministration of DPP-4 inhibitor and insulin therapy does not further reduce the risk of cardiovascular events compared with DPP-4 inhibitor therapy in diabetic foot patients: a nationwide population-based study
Yi-Hsuan Lin, Yu-Yao Huang, Yi-Ling Wu, Cheng-Wei Lin, Pei-Chun Chen, Chee Jen Chang, Sheng-Hwu Hsieh, Jui-Hung Sun, Szu-Tah Chen, Chia-Hung Lin
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Postmeal increment in intact glucagon-like peptide 1 level, but not intact glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide levels, is inversely associated with metabolic syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes
Soyeon Yoo, Eun-Jin Yang, Sang Ah Lee, Gwanpyo Koh
Endocrine Research.2018; 43(1): 47. CrossRef - Dipeptidyl Peptidase‐4 Inhibitors and Heart Failure Exacerbation in the Veteran Population: An Observational Study
Michael R. Cobretti, Benjamin Bowman, Ted Grabarczyk, Emily Potter
Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy.2018; 38(3): 334. CrossRef - Effects of a Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitor Sitagliptin on Glycemic Control and Lipoprotein Metabolism in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (GLORIA Trial)
Daisaku Masuda, Takuya Kobayashi, Masami Sairyou, Hiroyuki Hanada, Tohru Ohama, Masahiro Koseki, Makoto Nishida, Norikazu Maeda, Shinji Kihara, Tatsuya Minami, Koji Yanagi, Yasushi Sakata, Shizuya Yamashita
Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis.2018; 25(6): 512. CrossRef - Management of diabetes in older adults
G. Sesti, R. Antonelli Incalzi, E. Bonora, A. Consoli, A. Giaccari, S. Maggi, G. Paolisso, F. Purrello, G. Vendemiale, N. Ferrara
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2018; 28(3): 206. CrossRef - DPP4 inhibitors and cardiovascular outcomes: safety on heart failure
Chang Xia, Aditya Goud, Jason D’Souza, CHanukya Dahagam, Xiaoquan Rao, Sanjay Rajagopalan, Jixin Zhong
Heart Failure Reviews.2017; 22(3): 299. CrossRef - Sodium Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibition in Heart Failure
Yuliya Lytvyn, Petter Bjornstad, Jacob A. Udell, Julie A. Lovshin, David Z.I. Cherney
Circulation.2017; 136(17): 1643. CrossRef - Antidiabetic medications use trends in an Andalusian region from 2001 to 2014
Rocío López-Sepúlveda, María Ángeles García Lirola, Esther Espínola García, Jose María Jurado Martínez, Salvadora Martín Sances, Sonia Anaya Ordóñez, José Cabeza Barrera
Primary Care Diabetes.2017; 11(3): 254. CrossRef - The regulatory role of DPP4 in atherosclerotic disease
Lihua Duan, Xiaoquan Rao, Chang Xia, Sanjay Rajagopalan, Jixin Zhong
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Guidelines on the management of arterial hypertension and related comorbidities in Latin America
Journal of Hypertension.2017; 35(8): 1529. CrossRef - Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 and Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibition: Promise of a Dynamic Duo
Ildiko Lingvay
Endocrine Practice.2017; 23(7): 831. CrossRef - Assessment of the Risk of Hospitalization for Heart Failure With Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors, Saxagliptin, Alogliptin, and Sitagliptin in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes, Using an Alternative Measure to the Hazard Ratio
Masayuki Kaneko, Mamoru Narukawa
Annals of Pharmacotherapy.2017; 51(7): 570. CrossRef - Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and cancer risk in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
Ming Zhao, Jiayi Chen, Yanyan Yuan, Zuquan Zou, Xiaolong Lai, Daud M Rahmani, Fuyan Wang, Yang Xi, Qin Huang, Shizhong Bu
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - High circulating plasma dipeptidyl peptidase- 4 levels in non-obese Asian Indians with type 2 diabetes correlate with fasting insulin and LDL-C levels, triceps skinfolds, total intra-abdominal adipose tissue volume and presence of diabetes: a case–control
Shajith Anoop, Anoop Misra, Surya Prakash Bhatt, Seema Gulati, Ravindra Mohan Pandey, Harsh Mahajan
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2017; 5(1): bmjdrc-2017-000393. CrossRef - Vildagliptin reduces plasma stromal cell‐derived factor‐1α in patients with type 2 diabetes compared with glimepiride
Kyeong Seon Park, SooHeon Kwak, Young Min Cho, Kyong Soo Park, Hak C Jang, Seong Yeon Kim, Hye Seung Jung
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2017; 8(2): 218. CrossRef - New peroral antidiabetic drugs and heart failure
Jana Jiráčková, Alena Šmahelová
Interní medicína pro praxi.2016; 18(2): 78. CrossRef - Plasma DPP4 activity is associated with no-reflow and major bleeding events in Chinese PCI-treated STEMI patients
Jing Wei Li, Yun Dai Chen, Wei Ren Chen, Jing Jing, Jie Liu, Yong Qiang Yang
Scientific Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Sitagliptin and risk of heart failure hospitalization in patients with type 2 diabetes on dialysis: A population-based cohort study
Yi-Chih Hung, Che-Chen Lin, Wei-Lun Huang, Man-Ping Chang, Ching-Chu Chen
Scientific Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiovascular efficacy of sitagliptin in patients with diabetes at high risk of cardiovascular disease: a 12-month follow-up
Takashi Nakamura, Yoshitaka Iwanaga, Yuki Miyaji, Ryuji Nohara, Takao Ishimura, Shunichi Miyazaki
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Treating Diabetes in Patients with Heart Failure: Moving from Risk to Benefit
Ersilia M. DeFilippis, Michael M. Givertz
Current Heart Failure Reports.2016; 13(3): 111. CrossRef - Transcriptomic alterations in the heart of non-obese type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats
Márta Sárközy, Gergő Szűcs, Veronika Fekete, Márton Pipicz, Katalin Éder, Renáta Gáspár, Andrea Sója, Judit Pipis, Péter Ferdinandy, Csaba Csonka, Tamás Csont
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2016;[Epub] CrossRef
- Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor Use is Associated with a Reduced Risk of Heart Failure Hospitalization in Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Real-World Study on a Diverse Urban Population

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





